Integrated Stress Response in Human Islets during Early T1D
Contact PI: Raghu Mirmira, MD, PhD, University of Chicago (U01 DK127786)
Decio Eizirik, PhD, Investigator, Indiana Biosciences Research Institute
Carmella Evans-Molina, MD, Investigator, Indiana University
Thomas Metz, PhD, Investigator, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Bobbie-Jo Webb-Robinson, PhD, Investigator, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Sasanka Ramandha, PhD, Investigator, University of Alabama at Birmingham
Scott Oakes, PhD, Co-Investigator, University of Chicago
Sarah Tersey, PhD, Co-Investigator, University of Chicago
Manami Hara, PhD, Co-Investigator, University of Chicago
Ernesto Nakayasu, PhD, Co-Investigator, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory
Emily Sims, MD, Co-Investigator, Indiana University
Wenting Wu, PhD, Co-Investigator, Indiana University
Xiaoyong Lei, PhD, Co-Investigator, University of Alabama at Birmingham
Start Date: September 15, 2020
End Date: December 2025
Abstract
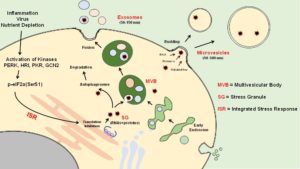
The pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes (T1D) encompasses a spectrum ranging from aggressive autoimmunity toward islet β cells to defects in β-cell function that arise from inflammation. A perspective that has been gaining traction in recent years posits that intracellular signaling pathways arising from the β cell response to inflammation can lead to the production of aberrant proteins that serve as neoantigens that initiate or exacerbate autoimmunity. This perspective has prompted our Team to identify and intervene in intracellular signaling pathways that affect β-cell resilience as T1D progresses from the presymptomatic to symptomatic stages. This proposal takes a multidisciplinary Team Science approach that is responsive to RFA-DK-19-024 to define and intervene in early T1D disease processes affecting human islets. The integrated stress response (ISR) is a cytoprotective process whereby environmental stress signals are transduced intracellularly to activate a host of eIF2α kinases. The phosphorylation of eIF2α halts general mRNA translation initiation in an effort to redirect energy expenditure to mitigate the prevailing stress. The translationally inhibited mRNAs and their associated proteins are sequestered into intracellular stress granules (SGs), the formations of which are thought to divert cellular signaling toward an emergency response. Our preliminary data suggest that the ISR is activated in islets during early T1D, and that the pathway linking membrane-derived lipids to the production of proinflammatory lipid intermediates may trigger the ISR and the formation of SGs. We hypothesize that the activation of the ISR and formation of SGs is an early cellular response initiating β cell stress in T1D that determines cell survival and can be monitored in pre- and early T1D individuals with minimal invasiveness. Our collaborative Team will test this hypothesis through the following aims: Aim 1: Define the mechanisms of stress granule formation and their fate upon activation of the integrated stress response in human islets. Aim 2: Determine the molecular events linking lipid metabolism, activation of the ISR, and stress granule formation in human islets. Aim 3: Identify protein, RNA, and lipid cargo in EVs as putative biomarkers of the human islet integrated stress response and T1D risk. This application leverages the expertise of 6 Multi-PIs in β-cell biology, lipid and eicosanoid biology, functional genomics, proteomics, computational modeling, and clinical islet studies. The impact of this project will be to deliver new knowledge on an unstudied stress pathway in human islets and to identify and validate biomarker panels that reflect this stress state.
Publications
- Challenges and Opportunities in State-of-the-Art Proteomics Analysis for Biomarker Development From Plasma Extracellular Vesicles
- Proinflammatory Stress Activates Neutral Sphingomyelinase 2-Based Generation of a Ceramide-Enriched β-Cell EV Subpopulation
- The integrated stress response promotes macrophage inflammation and migration in autoimmune diabetes
- Differential immune- and apoptosis-related gene signatures in pancreatic alpha and beta cells contribute to their fate in type 1 diabetes
- LONP1 loss causes mitochondrial mayhem in β-cells
- Insulin post-transcriptional regulation via PARP12-mediated ADP- ribosylation
- Molecular and Inflammatory Etiologies of ß Cell Dysfunction in Type 1 Diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes presenting in adults: Trends, diagnostic challenges and unique features
- Exercise-induced meteorin-like protein protects human pancreatic beta cells from cytokine-induced apoptosis
- The type 1 diabetes candidate genes PTPN2 and BACH2 regulate novel IFN-α-induced crosstalk between the JAK/STAT and MAPKs pathways in human beta cells
- Data from a multi-year targeted proteomics study of a longitudinal birth cohort of type 1 diabetes
- Dissecting tumor transcriptional heterogeneity from single-cell RNA-seq data by generalized binary covariance decomposition
- The N6-methyladenosine RNA epigenetic modification modulates the amplification of coxsackievirus B1 in human pancreatic beta cells
- Changes in immunofluorescence staining during islet regeneration in a cystic fibrosis-related diabetes (CFRD) ferret model
- LRH-1/NR5A2 targets mitochondrial dynamics to reprogram type 1 diabetes macrophages and dendritic cells into an immune tolerance phenotype
- Trajectory of beta cell function and insulin clearance in stage 2 type 1 diabetes: natural history and response to teplizumab
- β-Cell gene expression stress signatures in types 1 and 2 diabetes
- 12-Lipoxygenase inhibition delays onset of autoimmune diabetes in human gene replacement mice
- Beta cell extracellular vesicle PD-L1 as a novel regulator of CD8+ T cell activity and biomarker during the evolution of type 1 diabetes
- Emerging concepts and success stories in type 1 diabetes research: a roadmap for a bright future
- RNA Splicing Events in Circulation Distinguish Individuals with and without New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes
- Exploring new frontiers in type 1 diabetes through advanced mass-spectrometry-based molecular measurements
- Sodium butyrate prevents cytokine-induced β-cell dysfunction through restoration of stromal interaction molecule 1 expression and activation of store-operated calcium entry
- 12-Lipoxygenase inhibition suppresses islet immune and inflammatory responses and delays autoimmune diabetes in human gene replacement mice
- Diabetes mellitus-Progress and opportunities in the evolving epidemic
- Untangling the genetics of beta cell dysfunction and death in type 1 diabetes
- Beta cell dedifferentiation in type 1 diabetes: sacrificing function for survival?
- Inhibition of the eukaryotic initiation factor-2-α kinase PERK decreases risk of autoimmune diabetes in mice
- Unfolding emergency calls stress granules to the ER
- A Golden Hour and Golden Opportunity for β-Cell Preservation
- The integrated stress response in pancreatic development, tissue homeostasis, and cancer
- Pharmacological inhibition of tyrosine protein-kinase 2 reduces islet inflammation and delays type 1 diabetes onset in mice
- Proinflammatory stress activates neutral sphingomyelinase 2 based generation of a ceramide-enriched β cell EV subpopulation
- Islet autoantibodies as precision diagnostic tools to characterize heterogeneity in type 1 diabetes: a systematic review
- miR-146a-5p mediates inflammation-induced β cell mitochondrial dysfunction and apoptosis
- Interferons are key cytokines acting on pancreatic islets in type 1 diabetes
- Regulation of β-cell death by ADP-ribosylhydrolase ARH3 via lipid signaling in insulitis
- Reduction of chemokine CXCL9 expression by omega-3 fatty acids via ADP-ribosylhydrolase ARH3 in MIN6 insulin-producing cells
- A fast and sensitive size-exclusion chromatography method for plasma extracellular vesicle proteomic analysis
- Stress and human health in diabetes: A report from the 19(th) Chicago Biomedical Consortium symposium
- Mapping the daily rhythmic transcriptome in the diabetic retina
- Local dialogues between the endocrine and exocrine cells in the pancreas
- Discordant Effects of Polyamine Depletion by DENSpm and DFMO on β-cell Cytokine Stress and Diabetes Outcomes in Mice
- Advanced Imaging Techniques for the Characterization of Subcellular Organelle Structure in Pancreatic Islet β Cells
- Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors Prevent Cytokine-Induced β Cell Dysfunction Through Restoration of Stromal Interaction Molecule 1 Expression and Activation of Store-Operated Calcium Entry
- RedRibbon: A new rank-rank hypergeometric overlap for gene and transcript expression signatures
- Protection of β cells against pro-inflammatory cytokine stress by the GDF15-ERBB2 signaling
- A proteomic meta-analysis refinement of plasma extracellular vesicles
- Stress-induced β cell early senescence confers protection against type 1 diabetes
- Inhibition of polyamine biosynthesis preserves β cell function in type 1 diabetes
- Interferon-α promotes neo-antigen formation and preferential HLA-B-restricted antigen presentation in pancreatic β-cells
- Systematic review of type 1 diabetes biomarkers reveals regulation in circulating proteins related to complement, lipid metabolism, and immune response
- Fatty acid-mediated signaling as a target for developing type 1 diabetes therapies
- SERCA2 regulates proinsulin processing and processing enzyme maturation in pancreatic beta cells
- Stromal Interaction Molecule 1 Maintains β Cell Identity and Function in Female Mice through Preservation of G Protein-Coupled Estrogen Receptor 1 Signaling
- GLP-1R agonists demonstrate potential to treat Wolfram syndrome in human preclinical models
- Plasma protein biomarkers predict the development of persistent autoantibodies and type 1 diabetes 6 months prior to the onset of autoimmunity
- Pancreatic regional blood flow links the endocrine and exocrine diseases
- Analysis of a macrophage carbamylated proteome reveals a function in post-translational modification crosstalk
- Title: β Cell microRNAs Function as Molecular Hubs of Type 1 Diabetes Pathogenesis and as Biomarkers of Diabetes Risk
- Screening and prevention of type 1 diabetes: Where are we?
- β-Cell Function and Insulin Sensitivity in Youth With Early Type 1 Diabetes From a 2-Hour 7-Sample OGTT
- Deletion of the Unfolded Protein Response Transducer IRE1α Is Detrimental to Aging Photoreceptors and to ER Stress-Mediated Retinal Degeneration
- Why does the immune system destroy pancreatic β-cells but not α-cells in type 1 diabetes?
- Integrated Physiology of the Exocrine and Endocrine Compartments in Pancreatic Diseases: Workshop Proceedings
- Inhibition of the type 1 diabetes candidate gene PTPN2 aggravates TNF-α-induced human beta cell dysfunction and death
- BCL-XL Overexpression Protects Pancreatic β-Cells against Cytokine- and Palmitate-Induced Apoptosis
- Protocol to isolate immune cells from mouse pancreatic lymph nodes and whole pancreas for mass cytometric analyses
- Acute Recurrent Pancreatitis in a Child With INS-Related Monogenic Diabetes and a Heterozygous Pathogenic CFTR Mutation
- A discovery-based proteomics approach identifies protein disulphide isomerase (PDIA1) as a biomarker of β cell stress in type 1 diabetes
- ADAR1-dependent editing regulates human β cell transcriptome diversity during inflammation
- Mining the transcriptome of target tissues of autoimmune and degenerative pancreatic β-cell and brain diseases to discover therapies
- Inside the β Cell: Molecular Stress Response Pathways in Diabetes Pathogenesis
- The type 1 diabetes gene TYK2 regulates β-cell development and its responses to interferon-α
- Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines Promote the Transcription of Circular RNAs in Human Pancreatic β Cells
- Transcription and splicing regulation by NLRC5 shape the interferon response in human pancreatic β cells
- Precision medicine in type 1 diabetes
- In depth functional characterization of human induced pluripotent stem cell-derived beta cells in vitro and in vivo
- Predicting Misdiagnosed Adult-onset Type 1 Diabetes Using Machine Learning
- The Protective Action of Metformin against Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine-Induced Human Islet Cell Damage and the Mechanisms Involved
- Extracellular vesicles in β cell biology: Role of lipids in vesicle biogenesis, cargo, and intercellular signaling
- Does the Gut Microbiome Play a Role in Obesity in Type 1 Diabetes? Unanswered Questions and Review of the Literature
- Type I but Not Type II Calreticulin Mutations Activate the IRE1α/XBP1 Pathway of the Unfolded Protein Response to Drive Myeloproliferative Neoplasms
- Proinflammatory signaling in islet β cells propagates invasion of pathogenic immune cells in autoimmune diabetes
- Role of Polyamines and Hypusine in β Cells and Diabetes Pathogenesis
- Nmp4, a Regulator of Induced Osteoanabolism, Also Influences Insulin Secretion and Sensitivity
- GDF15: a potential therapeutic target for type 1 diabetes
- HOMA2-B enhances assessment of type 1 diabetes risk among TrialNet Pathway to Prevention participants
- The Deterrence of Rapid Metabolic Decline Within 3 Months After Teplizumab Treatment in Individuals at High Risk for Type 1 Diabetes
- CD8(+) T Cells Variably Recognize Native Versus Citrullinated GRP78 Epitopes in Type 1 Diabetes
- Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes: Current Understanding and Challenges
- The Impact of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines on Alternative Splicing Patterns in Human Islets
- A Humanized Mouse Strain That Develops Spontaneously Immune-Mediated Diabetes
- TIGER: The gene expression regulatory variation landscape of human pancreatic islets
- Deoxyhypusine synthase promotes a pro-inflammatory macrophage phenotype
- From Pancreatic β-Cell Gene Networks to Novel Therapies for Type 1 Diabetes
- The pancreatic β cell response to secretory demands and adaption to stress
- SARS-CoV-2 infection of islet β cells: Evidence and implications
- Tutorial: best practices and considerations for mass-spectrometry-based protein biomarker discovery and validation
- 100 years of insulin: celebrating the past, present and future of diabetes therapy
- 12-Lipoxygenase governs the innate immune pathogenesis of islet inflammation and autoimmune diabetes
- β-Cell pre-mir-21 induces dysfunction and loss of cellular identity by targeting transforming growth factor beta 2 (Tgfb2) and Smad family member 2 (Smad2) mRNAs
- A functional genomic approach to identify reference genes for human pancreatic beta cell real-time quantitative RT-PCR analysis
- Imatinib therapy for patients with recent-onset type 1 diabetes: a multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 2 trial
- Regulation of Tissue Inflammation by 12-Lipoxygenases
- Early impairment of insulin sensitivity, β-cell responsiveness, and insulin clearance in youth with Stage 1 type 1 diabetes
- Not so sweet and simple: impacts of SARS-CoV-2 on the β cell
- In Vivo and In Situ Approach to Study Islet Microcirculation: A Mini-Review
- Endogenous mitochondrial double-stranded RNA is not an activator of the type I interferon response in human pancreatic beta cells
- Cell-Free DNA Fragments as Biomarkers of Islet β-Cell Death in Obesity and Type 2 Diabetes
- Proinsulin:C-peptide ratio trajectories over time in relatives at increased risk of progression to type 1 diabetes
- Heterogeneity of Diabetes: β-Cells, Phenotypes, and Precision Medicine: Proceedings of an International Symposium of the Canadian Institutes of Health Research’s Institute of Nutrition, Metabolism and Diabetes and the U.S. National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases
- Gene expression signatures of target tissues in type 1 diabetes, lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, and rheumatoid arthritis
- The RNA-binding profile of the splicing factor SRSF6 in immortalized human pancreatic β-cells
- Implications of Integrated Pancreatic Microcirculation: Crosstalk between Endocrine and Exocrine Compartments
- Novel genetic risk factors influence progression of islet autoimmunity to type 1 diabetes
- Prediction of the development of islet autoantibodies through integration of environmental, genetic, and metabolic markers
- Probing islet stress in type 1 diabetes
- Integrated Pancreatic Blood Flow: Bidirectional Microcirculation Between Endocrine and Exocrine Pancreas

