HPAP T2D: Human Pancreas Analysis Program
Contact PI: Klaus Kaestner, PhD, University of Pennsylvania (U01DK123594)
Ali Naji, MD, PhD, Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Mark Atkinson, PhD Investigator, University of Florida
Al Powers, MD, Investigator, Vanderbilt University
Doris Stoffers, MD, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Anna Gloyn, PhD, co-Investigator, Stanford University
Parker Wilson, MD, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Golnaz Vahedi, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Babak Faryabi, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Start Date: September 30, 2019
Abstract
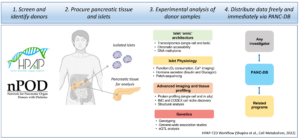
The past decades have seen a dramatic improvement in our ability to phenotype and molecularly profile human tissues relevant to the etiology of type 2 diabetes with unprecedented resolution, at the genomic, epigenomic, protein, and functional levels. Here we will employ state-of-the-art technologies to determine all aspects of pancreas biology as it pertains to type 2 diabetes, profile human pancreatic islets with multiple assay modalities, and make the vast data accumulated available through the highly accessible PANC-DB. This comprehensive profiling of the natural history of Type 2 diabetes will pave the way for future discoveries of new treatment modalities for diabetes.
 |
 |
Meet the Grant Team
Investigators |
|
Klaus Kaestner, PhDUniversity of Pennsylvania |
Ali Naji, MD, PhDUniversity of Pennsylvania |
Ben Voight, PhDUniversity of Pennsylvania |
|
Doris Stoffers, MD, PhDUniversity of Pennsylvania |
Jason Moore, PhDUniversity of Pennsylvania
|
Michael Feldman, MD, PhDUniversity of Pennsylvania
|
Publications
- Supervised machine learning identifies impaired mitochondrial quality control in β cells with development of type 2 diabetes
- Altered immune and metabolic molecular pathways drive islet cell dysfunction in human type 1 diabetes
- Single-cell multiome and spatial profiling reveals pancreas cell type-specific gene regulatory programs of type 1 diabetes progression
- Integrative single-cell multi-omics profiling of human pancreatic islets identifies T1D-associated genes and regulatory signals
- The antigen presentation landscape of cytokine-stressed human pancreatic islets
- Epigenetic adaptation of beta cells across lifespan and disease: age-related demethylation is advanced in type 2 diabetes
- Spatial transcriptomics from pancreas and local draining lymph node tissue reveals a lymphotoxin-β signature in human type 1 diabetes
- Immune perturbations in human pancreas lymphatic tissues prior to and after type 1 diabetes onset
- Functional and Mechanistic Explanation for the Unique Clinical Success of the Glucokinase Activator Dorzagliatin in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
- Closing the Gap Between Vision and Victory in Type 1 Diabetes: The NIDDK Human Islet Research Network (HIRN) Initiative
- Single-cell multiome and spatial profiling reveals pancreas cell type-specific gene regulatory programs driving type 1 diabetes progression
- IFN-α Induces Heterogenous ROS Production in Human β-Cells
- The XCL1/XCR1 axis is upregulated in type 1 diabetes and aggravates its pathogenesis
- TMEM55A-mediated PI5P signaling regulates α-cell actin depolymerization and glucagon secretion
- G6PC2 controls glucagon secretion by defining the set point for glucose in pancreatic α cells
- Heterogeneous endocrine cell composition defines human islet functional phenotypes
- The IsletTester mouse: an immunodeficient model with stable hyperglycemia for the study of human islets
- Sex-specific regulatory architecture of pancreatic islets from subjects with and without type 2 diabetes
- Human peripancreatic adipose tissue paracrine signaling impacts insulin secretion, blood flow, and gene transcription
- HumanIslets.com: Improving accessibility, integration, and usability of human research islet data
- Immune perturbations in human pancreas lymphatic tissues prior to and after type 1 diabetes onset
- Single cell multiome profiling of pancreatic islets reveals physiological changes in cell type-specific regulation associated with diabetes risk
- Single-cell multi-omic and spatial profiling of human kidneys implicates the fibrotic microenvironment in kidney disease progression
- No evidence for persistent enteroviral B infection of pancreatic islets in type 1 diabetic and pre-diabetic patients from RNA-Seq data
- Identification of unique cell type responses in pancreatic islets to stress
- HumanIslets: An integrated platform for human islet data access and analysis
- AnnoSpat annotates cell types and quantifies cellular arrangements from spatial proteomics
- NKX2-2 based nuclei sorting on frozen human archival pancreas enables the enrichment of islet endocrine populations for single-nucleus RNA sequencing
- DNA methylation-based assessment of cell composition in human pancreas and islets
- RFX6 maintains gene expression and function of adult human islet α cells
- Exocrine pancreas in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: different patterns of fibrosis, metaplasia, angiopathy, and adiposity
- Benchmarking algorithms for joint integration of unpaired and paired single-cell RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data
- The leptin receptor has no role in delta-cell control of beta-cell function in the mouse
- An Integrated Map of Cell Type-Specific Gene Expression in Pancreatic Islets
- Pericyte dysfunction and impaired vasomotion are hallmarks of islets during the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes
- Inferring regulators of cell identity in the human adult pancreas
- An integrated map of cell type-specific gene expression in pancreatic islets
- Understanding islet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes through multidimensional pancreatic phenotyping: The Human Pancreas Analysis Program
- Aging compromises human islet beta cell function and identity by decreasing transcription factor activity and inducing ER stress
- 3D chromatin maps of the human pancreas reveal lineage-specific regulatory architecture of T2D risk
- Adaptation to chronic ER stress enforces pancreatic β-cell plasticity
- α Cell dysfunction in islets from nondiabetic, glutamic acid decarboxylase autoantibody-positive individuals
- Variant-to-gene-mapping analyses reveal a role for pancreatic islet cells in conferring genetic susceptibility to sleep-related traits
- Limited extent and consequences of pancreatic SARS-CoV-2 infection
- Islet Lymphocytes Maintain a Stable Regulatory Phenotype Under Homeostatic Conditions and Metabolic Stress
- Single-cell analysis of the human pancreas in type 2 diabetes using multi-spectral imaging mass cytometry
- What is a β cell? – Chapter I in the Human Islet Research Network (HIRN) Review Series
- Pancreatic islet reserve in type 1 diabetes
- SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Are Expressed in the Microvasculature and Ducts of Human Pancreas but Are Not Enriched in β Cells







