HPAP T1D: Human Pancreas Analysis Program for Type 1 Diabetes
Contact PI: Ali Naji, MD, PhD, University of Pennsylvania (UC4 DK112217)
Klaus Kaestner, PhD, Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Alvin Powers, MD, Investigator, Vanderbilt University
Mark Atkinson, PhD, Investigator, University of Florida
Doris Stoffers, MD, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Nina Luning-Prak, MD, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Mohammad Haj Dezfulian, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Todd Brusko, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Florida
Parker Wilson, MD, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Golnaz Vahedi, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Babak Faryabi, PhD, co-Investigator, University of Pennsylvania
Start Date: September 20, 2016
Abstract
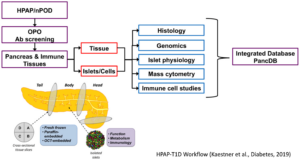
In 2016, the NIH NIDDK selected a multi-disciplinary team of investigators from three institutions (UPENN, Vanderbilt, University of Florida) to establish the pilot phase of the Human Pancreas Analysis Program (HPAP). Over the past three years, type 1 diabetes (T1D)-relevant tissues from more than 50 organ donors were profiled at the anatomic, physiologic, metabolic, immunologic, genomic and epigenomic levels. The resulting data were compiled and organized into the publicly accessible PANC-DB database and website. Here, we propose not only to continue, but to expand our efforts to apply and develop state-of-the-art technologies designed to phenotype and molecularly profile human tissues relevant to the etiology of T1D through a series of innovative efforts by six Cores. Core A (Pancreas Procurement and Islet Isolation) will procure/process pancreatic islets, pancreas and lymphoid organs, expand donor outreach (in collaboration with the well-established nPOD program) and increase the collection of non-pancreatic tissues. Core B (Physiological Phenotyping)will provide a comprehensive metabolic profile and probe the key regulatory steps that govern hormone secretion from the major pancreatic endocrine cell types. Core C (Immunobiology) will develop an immune atlas of peripancreatic lymphoid populations, obtain transcriptomic profiles of the T1D- specific T cells, and perform immune repertoire profiling of B and T cells in association with single cell and antigen-specific cell approaches. Core D (Advanced Molecular Profiling) will perform RNAseq, ATACseq and DNA methylome analysis on sorted alpha-cell, beta-cell and exocrine cell population as well as scRNAseq and scATACseq and carry out whole genome sequencing. In addition, islet endocrine and major lymphocyte populations will be quantified precisely using flow CyTOF. Core E (Tissue Analysis & Biobanking) will analyze pancreatic tissue architecture and immune cell/epithelial cell interactions using multiple modalities including imaging mass cytometry, multi-spectral imaging and CODEX. Complete image data will be made available via PancreatlasTM and PANC-DB. Finally, Core F (PANC-DB, Data Analysis and Integration) will expand the PANC-DB resource by adding new features that will make the public web page even more useful, as well as add a Computational Biology and Data Science Unit for applying state-of-the-art analytical tools, allowing for the integration and visualization of generated datasets using different experimental modalities such as multi-spectral imaging and omics technologies. In addition, Core F will continue to expand its outreach activities, exemplified via the deposition of transcriptome and epigenome data into the Diabetes Epigenome Atlas (DGA). HPAP-T1D will be directed by an experienced, collaborative multi-PI team that confers weekly and will meet in-person on a biannual basis in coordination with NIDDK leadership to review the progress of the entire program.
 |
 |
Meet the Grant Team
Investigators |
|
Ali Naji, MD, PhDUniversity of Pennsylvania |
Klaus Kaestner, PhDUniversity of Pennsylvania |
Alvin Powers, MDVanderbilt University |
Mark Atkinson, PhDUniversity of Florida |
|
Doris Stoffers, MD, PhDUniversity of Pennsylvania |
|
Mingder Yang, PhD University of Florida |
Irina Kusmartseva,University of Florida |
|
|
|
|
|
Publications
- CelLink: integrating single-cell multi-omics data with weak feature linkage and imbalanced cell populations
- Supervised machine learning identifies impaired mitochondrial quality control in β cells with development of type 2 diabetes
- Altered immune and metabolic molecular pathways drive islet cell dysfunction in human type 1 diabetes
- Single-cell multiome and spatial profiling reveals pancreas cell type-specific gene regulatory programs of type 1 diabetes progression
- The pathophysiology, presentation and classification of Type 1 diabetes
- Integrative single-cell multi-omics profiling of human pancreatic islets identifies T1D-associated genes and regulatory signals
- The antigen presentation landscape of cytokine-stressed human pancreatic islets
- A structure-guided approach to predict MHC-I restriction of T cell receptors for public antigens
- OLIVE Provides Rapid Visualization and Analysis of Chromatin Tracing Experiments
- Inference of multi-enhancer interactions in T lymphocytes using Hi-Cociety
- Epigenetic adaptation of beta cells across lifespan and disease: age-related demethylation is advanced in type 2 diabetes
- Single-Allele Chromatin Tracing Reveals Genomic Clustering of Paralogous Transcription Factors as a Mechanism for Developmental Robustness in T Cells
- Solution mapping of MHC-I:TCR interactions using a minimalistic protein system
- Spatial transcriptomics from pancreas and local draining lymph node tissue reveals a lymphotoxin-β signature in human type 1 diabetes
- Immune perturbations in human pancreas lymphatic tissues prior to and after type 1 diabetes onset
- Functional and Mechanistic Explanation for the Unique Clinical Success of the Glucokinase Activator Dorzagliatin in the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes
- The epigenetic landscape of fate decisions in T cells
- IFN-α Induces Heterogenous ROS Production in Human β-Cells
- Single-cell multiome and spatial profiling reveals pancreas cell type-specific gene regulatory programs driving type 1 diabetes progression
- The XCL1/XCR1 axis is upregulated in type 1 diabetes and aggravates its pathogenesis
- CryoEM structure of an MHC-I/TAPBPR peptide-bound intermediate reveals the mechanism of antigen proofreading
- TMEM55A-mediated PI5P signaling regulates α-cell actin depolymerization and glucagon secretion
- G6PC2 controls glucagon secretion by defining the set point for glucose in pancreatic α cells
- Targeting peptide antigens using a multiallelic MHC I-binding system
- Heterogeneous endocrine cell composition defines human islet functional phenotypes
- Sex-specific regulatory architecture of pancreatic islets from subjects with and without type 2 diabetes
- Human peripancreatic adipose tissue paracrine signaling impacts insulin secretion, blood flow, and gene transcription
- The Type 1 Diabetes T Cell Receptor and B Cell Receptor Repository in the AIRR Data Commons: a practical guide for access, use and contributions through the Type 1 Diabetes AIRR Consortium
- Thermal Denaturation of Fresh Frozen Tissue Enhances Mass Spectrometry Detection of Peptides
- HumanIslets.com: Improving accessibility, integration, and usability of human research islet data
- Immune perturbations in human pancreas lymphatic tissues prior to and after type 1 diabetes onset
- Human vascularized macrophage-islet organoids to model immune-mediated pancreatic β cell pyroptosis upon viral infection
- Single cell multiome profiling of pancreatic islets reveals physiological changes in cell type-specific regulation associated with diabetes risk
- Single-cell multi-omic and spatial profiling of human kidneys implicates the fibrotic microenvironment in kidney disease progression
- No evidence for persistent enteroviral B infection of pancreatic islets in type 1 diabetic and pre-diabetic patients from RNA-Seq data
- Identification of unique cell type responses in pancreatic islets to stress
- HumanIslets: An integrated platform for human islet data access and analysis
- AnnoSpat annotates cell types and quantifies cellular arrangements from spatial proteomics
- NKX2-2 based nuclei sorting on frozen human archival pancreas enables the enrichment of islet endocrine populations for single-nucleus RNA sequencing
- Modeling type 1 diabetes progression using machine learning and single-cell transcriptomic measurements in human islets
- Conformational plasticity of RAS Q61 family of neoepitopes results in distinct features for targeted recognition
- Disrupted RNA editing in beta cells mimics early-stage type 1 diabetes
- RFX6 maintains gene expression and function of adult human islet α cells
- Genetic risk converges on regulatory networks mediating early type 2 diabetes
- Checkpoint kinase 2 controls insulin secretion and glucose homeostasis
- Human Pseudoislet System for Synchronous Assessment of Fluorescent Biosensor Dynamics and Hormone Secretory Profiles
- An integrative single-cell multi-omics profiling of human pancreatic islets identifies T1D associated genes and regulatory signals
- Exocrine pancreas in type 1 and type 2 diabetes: different patterns of fibrosis, metaplasia, angiopathy, and adiposity
- Benchmarking algorithms for joint integration of unpaired and paired single-cell RNA-seq and ATAC-seq data
- HLA3DB: comprehensive annotation of peptide/HLA complexes enables blind structure prediction of T cell epitopes
- The leptin receptor has no role in delta-cell control of beta-cell function in the mouse
- Intrinsically disordered domain of transcription factor TCF-1 is required for T cell developmental fidelity
- An Integrated Map of Cell Type-Specific Gene Expression in Pancreatic Islets
- A Chicken Tapasin ortholog can chaperone empty HLA-B∗37:01 molecules independent of other peptide-loading components
- Pericyte dysfunction and impaired vasomotion are hallmarks of islets during the pathogenesis of type 1 diabetes
- The pathogenic “symphony” in type 1 diabetes: A disorder of the immune system, β cells, and exocrine pancreas
- Inferring regulators of cell identity in the human adult pancreas
- Human circulating and tissue-resident memory CD8(+) T cells
- Universal open MHC-I molecules for rapid peptide loading and enhanced complex stability across HLA allotypes
- Quantitative control of Ets1 dosage by a multi-enhancer hub promotes Th1 cell differentiation and protects from allergic inflammation
- A genomic data archive from the Network for Pancreatic Organ donors with Diabetes
- Integrating genetics with single-cell multiomic measurements across disease states identifies mechanisms of beta cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes
- Single-cell expression profiling of islets generated by the Human Pancreas Analysis Program
- The human α cell in health and disease
- Peeling the onion: another layer in the regulation of insulin secretion
- Integrated Physiology of the Exocrine and Endocrine Compartments in Pancreatic Diseases: Workshop Proceedings
- A beta cell subset with enhanced insulin secretion and glucose metabolism is reduced in type 2 diabetes
- An integrated map of cell type-specific gene expression in pancreatic islets
- Autoantibodies are highly prevalent in non-SARS-CoV-2 respiratory infections and critical illness
- Human pancreatic capillaries and nerve fibers persist in type 1 diabetes despite beta cell loss
- Computational workflow and interactive analysis of single-cell expression profiling of islets generated by the Human Pancreas Analysis Program
- Integration of single-cell multiomic measurements across disease states with genetics identifies mechanisms of beta cell dysfunction in type 2 diabetes
- Aging compromises human islet beta cell function and identity by decreasing transcription factor activity and inducing ER stress
- Understanding islet dysfunction in type 2 diabetes through multidimensional pancreatic phenotyping: The Human Pancreas Analysis Program
- d-Amino Acids and Classical Neurotransmitters in Healthy and Type 2 Diabetes-Affected Human Pancreatic Islets of Langerhans
- 3D chromatin maps of the human pancreas reveal lineage-specific regulatory architecture of T2D risk
- Every islet matters: improving the impact of human islet research
- Adaptation to chronic ER stress enforces pancreatic β-cell plasticity
- TCF-1 promotes chromatin interactions across topologically associating domains in T cell progenitors
- α Cell dysfunction in islets from nondiabetic, glutamic acid decarboxylase autoantibody-positive individuals
- Variant-to-gene-mapping analyses reveal a role for pancreatic islet cells in conferring genetic susceptibility to sleep-related traits
- Single-cell multi-omics analysis of human pancreatic islets reveals novel cellular states in type 1 diabetes
- Heterogenous impairment of α cell function in type 2 diabetes is linked to cell maturation state
- Islet Lymphocytes Maintain a Stable Regulatory Phenotype Under Homeostatic Conditions and Metabolic Stress
- Autoantibodies targeting cytokines and connective tissue disease autoantigens are common in acute non-SARS-CoV-2 infections
- Transcription factors combine to paint the methylation landscape
- Cellular and humoral immune responses following SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccination in patients with multiple sclerosis on anti-CD20 therapy
- New-onset IgG autoantibodies in hospitalized patients with COVID-19
- What is a β cell? – Chapter I in the Human Islet Research Network (HIRN) Review Series
- From type 1 diabetes biology to therapy: The Human Islet Research Network
- A New Hypothesis for Type 1 Diabetes Risk: The At-Risk Allele at rs3842753 Associates With Increased Beta-cell INS Messenger RNA in a Meta-Analysis of Single-Cell RNA-Sequencing Data
- Biological controls for standardization and interpretation of adaptive immune receptor repertoire profiling
- Deep immune profiling of MIS-C demonstrates marked but transient immune activation compared to adult and pediatric COVID-19
- Pancreatic islet reserve in type 1 diabetes
- TCR(+)/BCR(+) dual-expressing cells and their associated public BCR clonotype are not enriched in type 1 diabetes
- Remodeling the chromatin landscape in T lymphocytes by a division of labor among transcription factors
- Norovirus-Specific CD8(+) T Cell Responses in Human Blood and Tissues
- The Identity of Human Tissue-Emigrant CD8(+) T Cells
- SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Factors ACE2 and TMPRSS2 Are Expressed in the Microvasculature and Ducts of Human Pancreas but Are Not Enriched in β Cells
- Ten simple rules for writing a paper about scientific software
- Mining the Antibody Repertoire for Solutions to SARS-CoV-2
- Organisation of the human pancreas in health and in diabetes
- Embedding covariate adjustments in tree-based automated machine learning for biomedical big data analyses
- Islet transplantation in the subcutaneous space achieves long-term euglycaemia in preclinical models of type 1 diabetes
- Evaluating recommender systems for AI-driven biomedical informatics
- Comprehensive mapping of immune perturbations associated with severe COVID-19
- Discovery of 318 new risk loci for type 2 diabetes and related vascular outcomes among 1.4 million participants in a multi-ancestry meta-analysis
- A Human Pluripotent Stem Cell-based Platform to Study SARS-CoV-2 Tropism and Model Virus Infection in Human Cells and Organoids
- The Transcription Factor T-bet Resolves Memory B Cell Subsets with Distinct Tissue Distributions and Antibody Specificities in Mice and Humans
- High throughput pMHC-I tetramer library production using chaperone-mediated peptide exchange
- Sel1L-Hrd1 ER-associated degradation maintains β-cell identity via TGFβ signaling
- Genetic Variation in Type 1 Diabetes Reconfigures the 3D Chromatin Organization of T Cells and Alters Gene Expression.
- miRNA142-3p targets Tet2 and impairs Treg differentiation and stability in models of type 1 diabetes
- OMNIREP: Originating Meaning by Coevolving Encodings and Representations
- Exploration of a diversity of computational and statistical measures of association for genome-wide genetic studies
- Integration of genetic and clinical information to improve imputation of data missing from electronic health records
- ODAL: A one-shot distributed algorithm to perform logistic regressions on electronic health records data from multiple clinical sites
- Automated discovery of test statistics using genetic programming
- Multiplexed In Situ Imaging Mass Cytometry Analysis of the Human Endocrine Pancreas and Immune System in Type 1 Diabetes
- ImmuneDB, a Novel Tool for the Analysis, Storage, and Dissemination of Immune Repertoire Sequencing Data
- Benchmarking Relief-Based Feature Selection Methods for Bioinformatics Data Mining
- Leveraging epigenomics and contactomics data to investigate SNP pairs in GWAS
- Improving machine learning reproducibility in genetic association studies with proportional instance cross validation (PICV)
- Investigating the parameter space of evolutionary algorithms
- Data-driven advice for applying machine learning to bioinformatics problems
- A miRNA181a/NFAT5 axis links impaired T cell tolerance induction with autoimmune type 1 diabetes
- A Heuristic Method for Simulating Open-data of Arbitrary Complexity that can be used to Compare and Evaluate Machine Learning Methods
- Leveraging putative enhancer-promoter interactions to investigate two-way epistasis in Type 2 Diabetes GWAS
- PMLB: a Large Benchmark Suite for Machine Learning Evaluation and Comparison
- Evolutionarily derived networks to inform disease pathways










